Antwort How to design zero trust architecture? Weitere Antworten – How do you build Zero Trust architecture
Building a Zero Trust Architecture: 4 Best Practices
- Know your Architecture Including Users, Devices, and Services.
- Create Strong Device Identities.
- Focus Your Monitoring on Devices and Services.
- Don't Trust the Network, Including the Local Network.
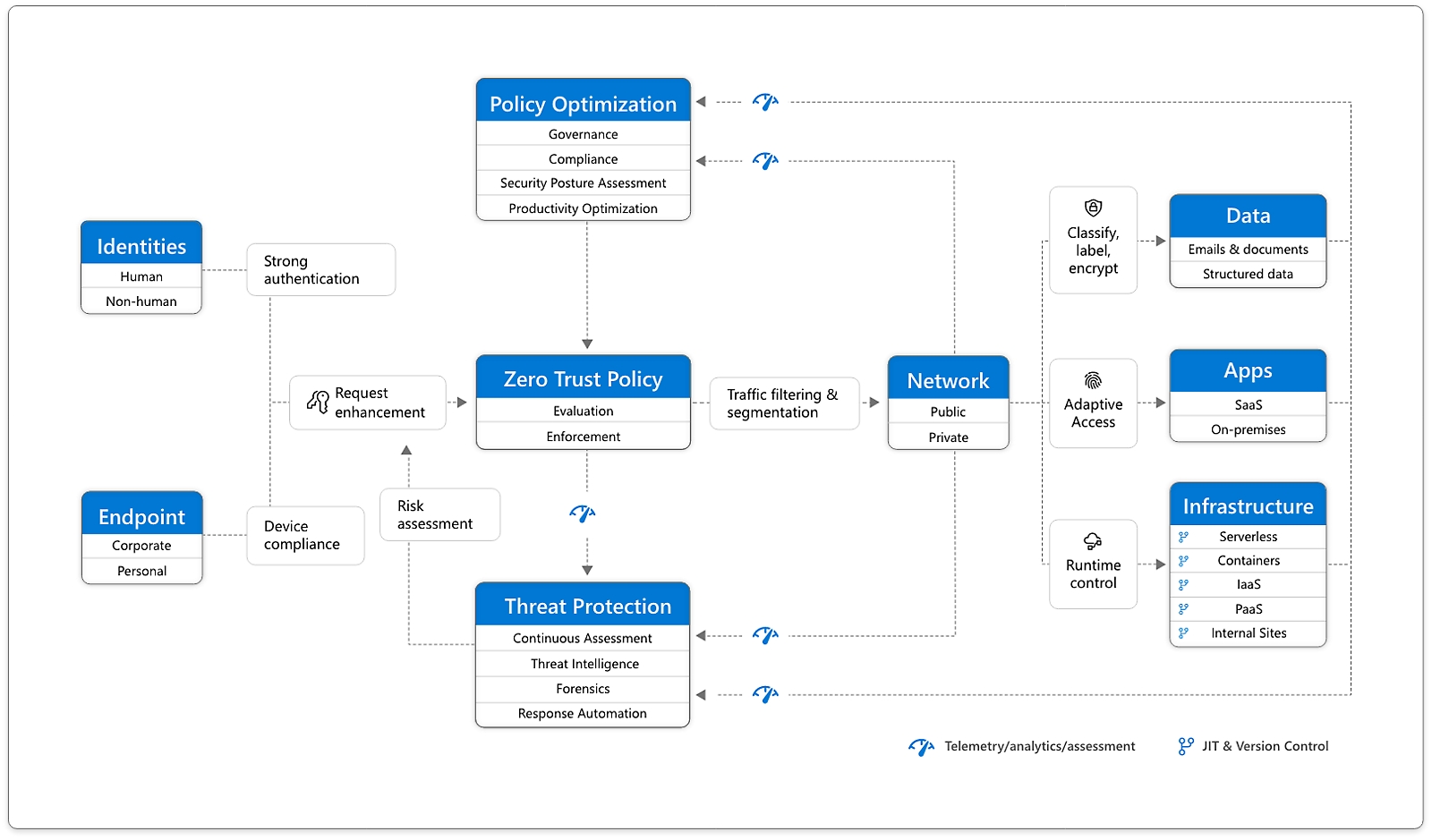
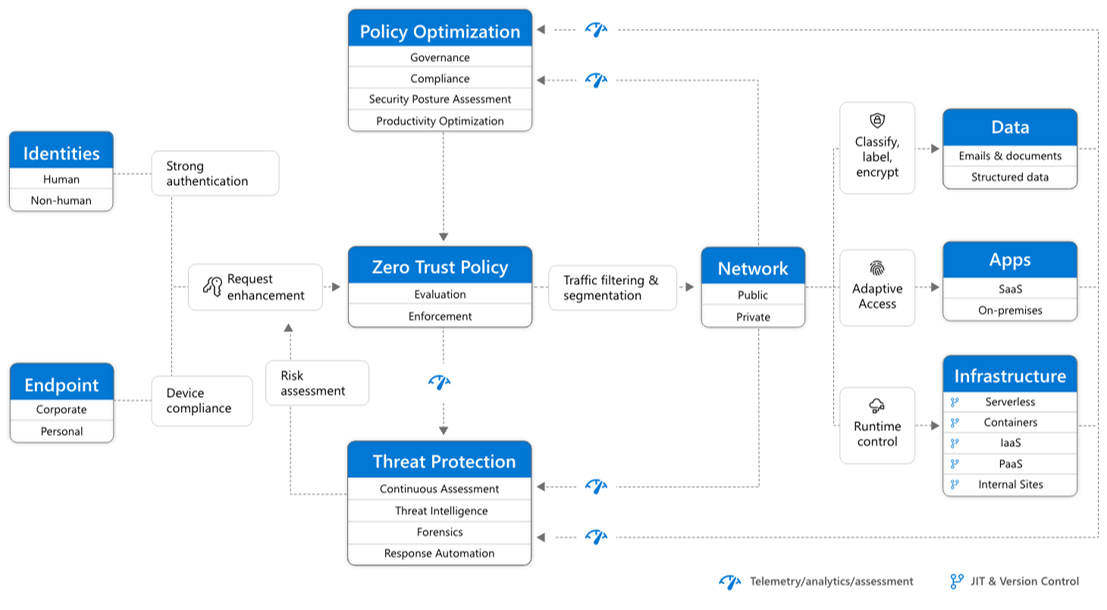
The seven pillars are: User, Device, Network & Environment, Application & Workload, Data, Automation & Orchestration, and Visibility & Analytics. Each pillar requires certain criteria and objectives to achieve ZT enactment.The five pillars of zero-trust security are identity, device, network, application and workload and data.
Which are the starting points when designing a Zero Trust architecture : The Principles
- Know your architecture including users, devices, and services.
- Create a single strong user identity.
- Create a strong device identity.
- Authenticate everywhere.
- Know the health of your devices and services.
- Focus your monitoring on devices and services.
- Set policies according to value of the service or data.
Why is Zero Trust hard to implement
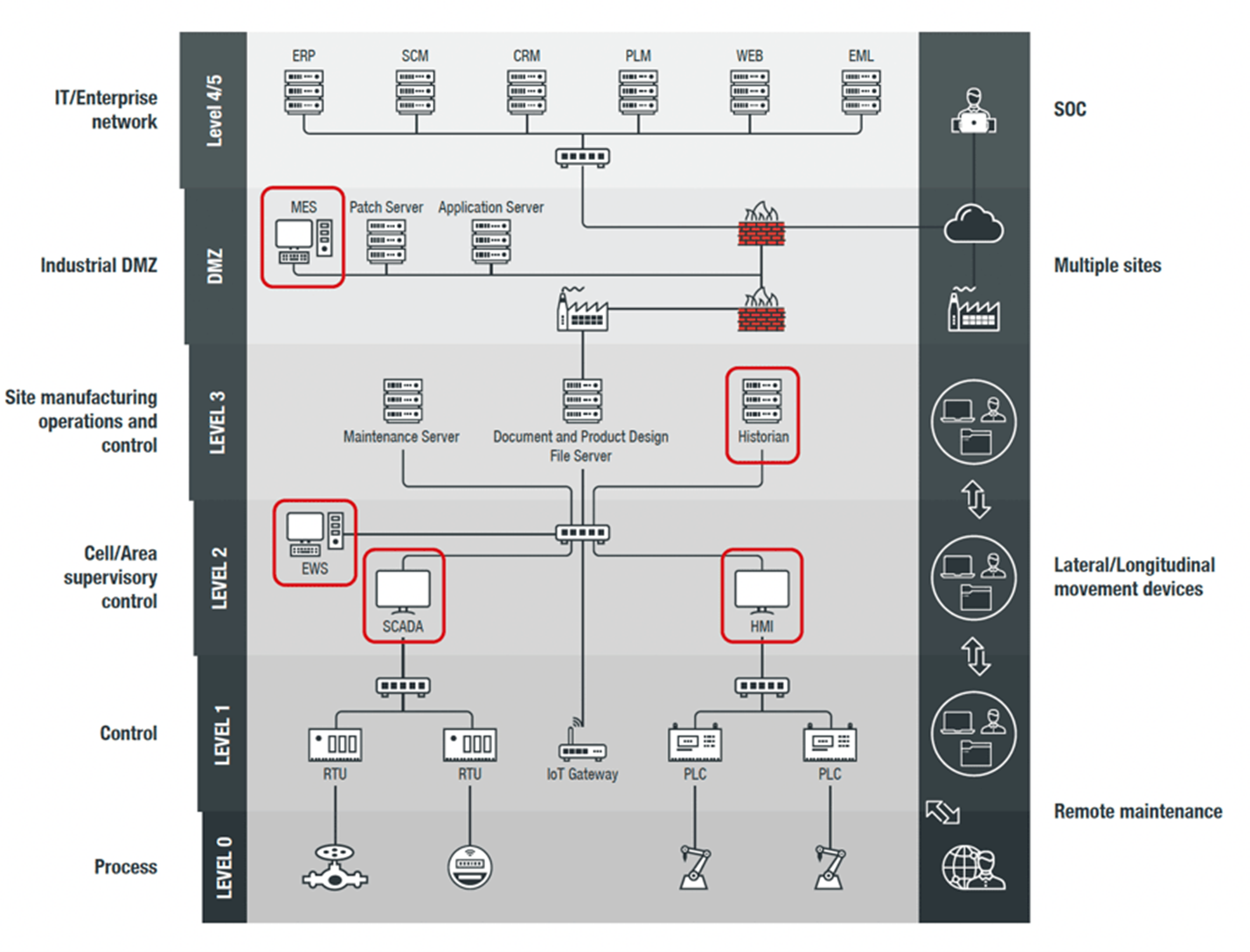
Here's where most security professionals run into difficulty with Zero Trust implementation: Complexity: To set up Zero Trust architecture, organizations need to have a complete picture of their data and workflows. Every single resource and endpoint needs identifying, access control, and monitoring.
What is an example of zero trust architecture : To illustrate this, let's use the famous prison on Alcatraz Island as an example. Alcatraz was designed to be a maximum-security prison, and it was built with the concept of zero trust in mind. Like in a zero-trust architecture, Alcatraz assumed that no one, even the prison staff, could be trusted.
There are three key components in a zero trust network: user/application authentication, device authentication, and trust.
The guiding principles of Zero Trust
- Verification. Verify and validate every action by continuously authorizing attributes and context.
- Enforcement. Enforce least privileged access using a combination of 'Just-In-Time' (JIT) and 'Just Enough' (JE) access.
- Adoption.
- Identities.
- Devices.
- Applications.
- Data.
- Infrastructure.
What are the 3 foundational concepts of Zero Trust
Zero Trust seeks to address the following key principles based on the NIST guidelines: Continuous verification. Always verify access, all the time, for all resources. Limit the “blast radius.” Minimize impact if an external or insider breach does occur.The biggest challenge with Zero Trust is that it can be complex to implement. The fact that every user, device, and application must be authenticated and authorized adds an extra layer of complexity — particularly for organizations with a large number of users.A zero trust model requires defining who can access which areas of their network and create appropriate network segmentation—this requires careful planning and collaboration. Organizations will need to hire or allocate personnel to implement network segmentation and maintain it on an ongoing basis.
There are three key components in a zero trust network: user/application authentication, device authentication, and trust.
What is Zero Trust architecture for dummies : Zero trust basic principles
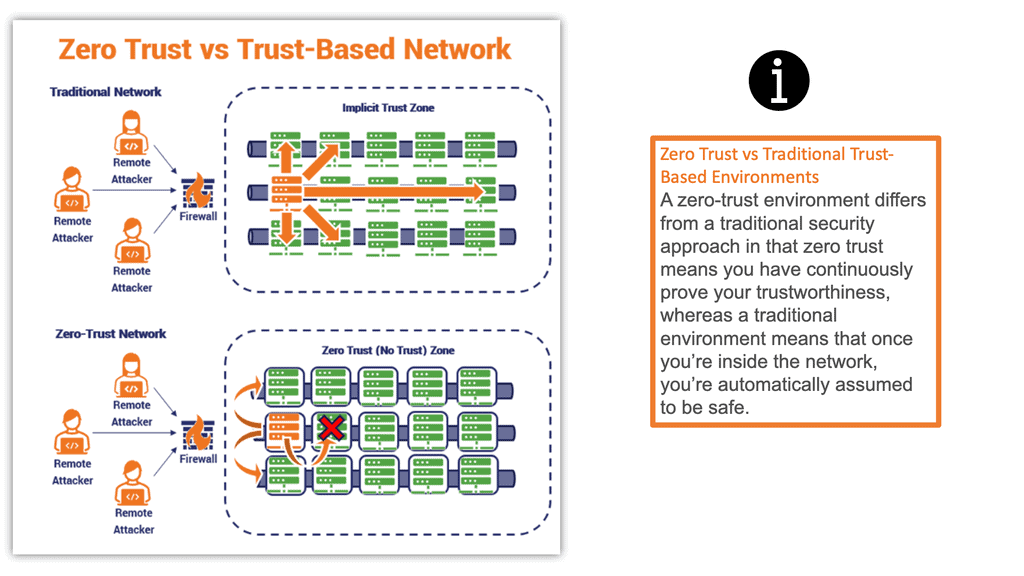
Do not trust network location or identity – traditional perimeter-only security operates with a single door for users to gain access to enterprise resources. Once authenticated, a user gains broad access to enterprise-owned assets. This practice opens the door for malicious actors as well.
What are the six pillars of Zero Trust : The Six Pillars of Zero Trust
- Identities.
- Devices.
- Applications.
- Data.
- Infrastructure.
- Networks.
Which three 3 of practices are core principles of Zero Trust
As business and technology continue to evolve, the three core principles of Zero Trust security remain consistent. Never trust. Always verify. Implement Zero Trust security for your business.
What's the Problem with Zero Trust Briefly: Zero trust presumes that no network connection, internal or external, can be trusted. Every user authenticates with multi-factor, every system's authentication is reverified multiple times on the network, and the default access policy for everything is 'deny'.The Six Pillars of Zero Trust
- Identities.
- Devices.
- Applications.
- Data.
- Infrastructure.
- Networks.
What is a real life example of zero trust architecture : To illustrate this, let's use the famous prison on Alcatraz Island as an example. Alcatraz was designed to be a maximum-security prison, and it was built with the concept of zero trust in mind. Like in a zero-trust architecture, Alcatraz assumed that no one, even the prison staff, could be trusted.